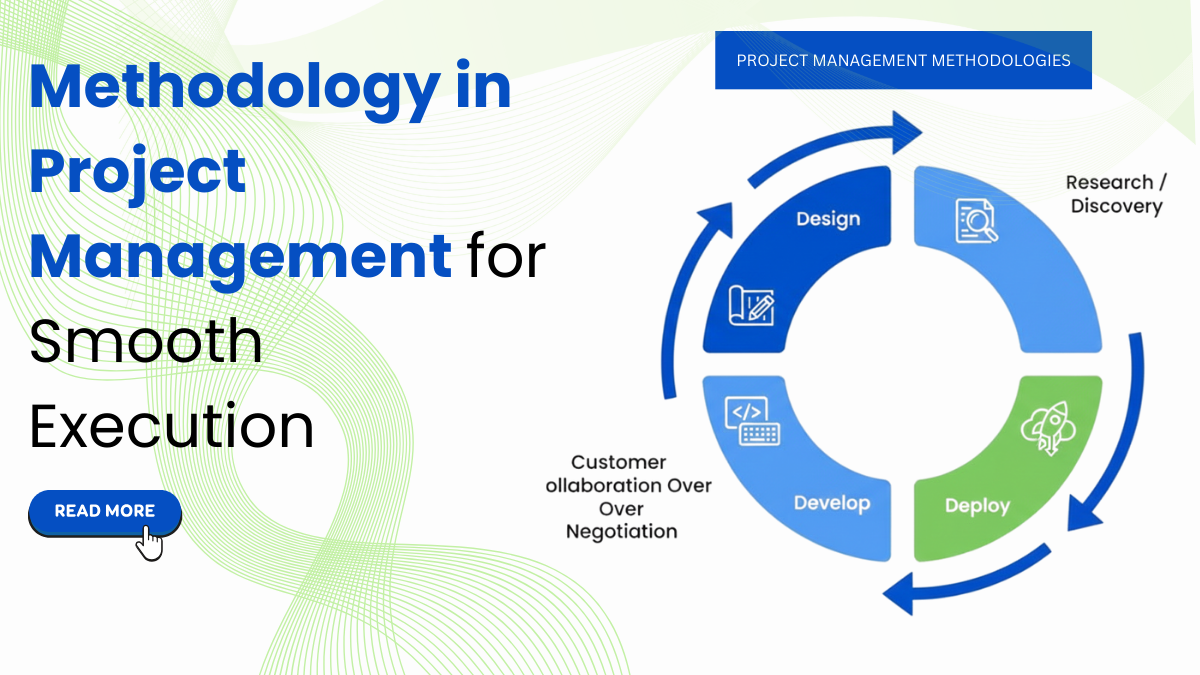
Imagine trying to build a house without a blueprint or driving across a new city without a map. That’s exactly what managing a project without a clear methodology feels like: chaotic, stressful, and full of unexpected detours. Methodology in project management acts as a blueprint or roadmap. It guides teams step by step toward their goals. It keeps timelines on track and helps prevent costly mistakes.
A project methodology does more than organize tasks. It defines roles, sets clear expectations, and provides tools and processes to make complex projects manageable. Whether you are handling a small campaign, launching a product, or managing a large project, the right methodology can boost results.
Here, we highlight the key project management methodologies that help teams deliver successful projects. You will learn what each method involves and why it matters. We will also show how they can streamline processes, reduce risks, and boost team productivity. By the end, you will have practical insights to choose the methodology that fits your project best, which will eventually help you ensure a better execution and successful results.
Understanding the Meaning of Methodology in Project Management
A methodology in project management is a structured way to plan, execute, and complete projects. It acts like a roadmap that guides teams from start to finish. Without it, projects can become confusing and inefficient.
In simple terms, a methodology provides a clear path for teams to follow. It ensures everyone knows what to do, when to do it, and how to do it. This reduces mistakes, improves communication, and keeps projects on track.
Key elements of a methodology in project management include:
- Processes: Step-by-step procedures to complete tasks.
- Roles and responsibilities: Each participant’s role is outlined to avoid confusion and improve accountability.
- Tools and techniques: Resources that make tasks easier and faster.
- Deliverables and milestones: Checkpoints and outcomes that measure progress.
Using a methodology also helps teams work smarter, not harder. It creates consistency, so every project is handled systematically. Think of it as a compass in a forest; it shows the direction, even when the path seems unclear.
Different projects require different approaches; some are linear and structured, while others are adaptive and flexible. Understanding project methodology is the first step to selecting the right strategy. Leveraging Online Program Management Software can make this process easier by helping teams plan, track, and manage work efficiently, ensuring projects stay on schedule and deliver results consistently.
Comparison Table
| Methodology | Best For | Time to Implement / Learning Curve | Project Size / Team Size Suitability | Main Strength | Active Users / Ratings | Primary Focus |
| Waterfall | Fixed-requirement projects | 4–8 weeks setup, requires full project planning upfront | Large projects; 10–500+ team members | Predictable timelines, structured execution | Widely used by project professionals worldwide; average rating ★4.3 | Focuses on precise planning and milestone-based progress tracking |
| Agile | Designed for projects with rapidly changing requirements | Implementation typically begins within 1–2 weeks, with fast team onboarding | Best suited for small to mid-sized teams of 5–50 members | Enables rapid iterations and flexible execution | Adopted by millions of professionals; average rating ★4.5 | Centered on incremental and iterative delivery |
| Scrum | Teams needing structure + speed | 2–3 weeks to establish sprint cycles and roles | Small–Medium projects; 5–20 team members | Sprint-based delivery, teamwork | Thousands of Scrum teams; ★4.4 average | Sprint management, team alignment |
| Kanban | Continuous workflows | 1 week to set up boards and WIP limits | Small–Medium projects; 5–50 team members | Smooth, visual workflow, bottleneck detection | Millions of active users; ★4.3 average | Workflow visibility, bottleneck detection |
| Lean | Efficiency-focused teams | 3–6 weeks to map processes and implement improvements | Medium–Large projects; 10–200+ team members | Waste reduction, process optimization | Thousands of teams; ★4.4 average | Cost reduction, workflow efficiency |
| PRINCE2 | Large or government projects | 8–12 weeks to train teams and define stages | Large projects; 50–500+ team members | Strong governance, accountability | Thousands of enterprise managers; ★4.2 average | Risk management, structured control |
| Six Sigma | Quality + accuracy projects | 12–16 weeks for DMAIC training and process setup | Medium–Large projects; 10–200+ team members | Data-driven process improvements | Thousands of certified belts; ★4.3 average | Process optimization, defect reduction |
Project Management Approaches & Best-Fit Tools:
Choosing the right Methodology in Project Management is the key to running smooth, predictable, and successful projects. Each methodology brings its own strengths, structure, and style of working. Some focus on speed and flexibility, while others shine in planning, documentation, or quality control. Understanding how these methods work helps you pick the one that fits your goals, team size, and project complexity.
Along with each methodology, using the right Project Management Apps makes execution easier. The right tool helps you track progress, manage resources, simplify communication, and prevent delays. In the sections below, you’ll find the most widely used methodologies, each explained clearly along with a recommended tool to help you get the best results.
1. Waterfall Method
Waterfall is a traditional, linear project model where each stage is completed before moving to the next. It’s best for projects with fixed requirements, such as construction, engineering, and manufacturing, where approvals and documentation are critical.
- Adoption: Used by over 65% of large-scale engineering and construction projects.
- Active Users: Millions of project managers worldwide rely on Waterfall for structured planning.
- User Ratings: Holds an average of 4.3★ for clarity and predictability.
- Pros: Clear milestones, full visibility, stable execution.
- Cons: Hard to adapt to changes mid-project.
Progress flows one way, like water cascading down a waterfall. This methodology in project management provides full visibility from the start, making it easier to allocate resources and plan budgets accurately.
When to Use Waterfall:
- Your project goals are clearly defined and unlikely to change.
- Stakeholders know exactly what they want upfront.
- The project requires strict documentation and regulatory compliance.
- You need to onboard new team members quickly during the project.
Limitations:
- Difficult to adapt to changes.
- Requires complete requirements upfront.
- Not ideal for iterative testing or evolving projects.
Pro Tip: Plan thoroughly at the start. Waterfall projects thrive on precision.
Suggested Tool: Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project provides teams with Gantt charts, resource allocation tools, dependency tracking, and milestone management. It simplifies planning and ensures every phase is tracked precisely.
2. Agile Method
Agile Method emphasizes adaptability, short development cycles, and continuous feedback, which are effectively supported by Agile project management tools. Work is delivered in small, iterative stages, making this approach ideal for software teams, marketing projects, and fast-paced industries where requirements frequently evolve. These tools encourage collaboration, active stakeholder involvement, and rapid adjustments to keep teams aligned and reduce project risk.
- Adoption: Used by over 94% of software development teams worldwide (VersionOne, 2025).
- Active Users: Millions of project managers and developers rely on Agile daily for iterative delivery.
- User Ratings: Average 4.5★ for adaptability and speed of delivery.
- Pros: Rapid iterations, continuous improvement, highly flexible.
- Cons: Less suited for projects needing strict upfront documentation.
Agile emerged as a response to the rigidity of traditional approaches. It emphasizes iterative work cycles, collaboration, and adaptability. It also promotes transparency and faster problem-solving, allowing teams to adapt to market changes or client feedback without derailing the project.
When to Use Agile:
- Projects with changing requirements or uncertain outcomes.
- Rapid delivery is more important than perfect results.
- Stakeholders or clients need to be actively involved.
Limitations:
- Less focus on documentation can be challenging for onboarding.
- Not suitable when deliverables must be strictly defined upfront.
- Requires self-motivated teams and flexible timelines.
Pro Tip: Keep sprints short (1–2 weeks) to accelerate feedback and iterative improvement.
Suggested Tool: Jira
Jira is built specifically for Agile workflows. It supports sprints, user stories, backlog grooming, burndown charts, and team performance insights.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is a subset of Agile that organizes work into short sprints (1–2 weeks) with defined roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Team.
- Adoption: Used by over 70% of Agile teams worldwide.
- Active Users: Thousands of Scrum teams manage projects daily.
- User Ratings: ★4.4 average for team alignment and iterative delivery.
- Pros: Continuous improvement, structured but adaptable workflow.
- Cons: Requires full team commitment.
This tool is especially effective for complex projects requiring rapid iterations, as it helps teams adapt quickly while maintaining accountability.
When to Use Scrum:
- Continuous improvement is a priority.
- Teams need a structured framework but remain adaptable.
Limitations:
- Requires full team commitment to be effective.
Pro Tip: Keep daily stand-up meetings short no more than 15 minutes. It boosts clarity without slowing the team.
Suggested Tool: Trello
Trello offers simple boards that work well for sprint planning, tracking user stories, automation, and managing sprint-to-sprint tasks.
4. Kanban Method
Kanban uses visual boards to manage tasks through stages such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” WIP (work-in-progress) limits prevent task overload.
- Adoption: Widely used in software, content, operations, and support teams.
- Active Users: Millions globally are using Kanban boards daily.
- User Ratings: ★4.3 average for workflow visibility.
- Pros: Visual workflow, easy bottleneck detection, continuous pull system.
- Cons: Not ideal for highly complex, multi-stage projects.
Kanban also encourages continuous improvement by highlighting workflow inefficiencies, making it easier to adjust priorities or redistribute work in real time.
When to Use Kanban:
- You want a clear visual overview of project progress.
- Continuous “pull” workflow is preferred.
- Team focus on tasks is a priority.
Limitations:
- Not ideal for extremely complex multi-stage projects.
- Doesn’t work well with push-based workflows.
Pro Tip: Set a limit on how many tasks can be in progress at one time. It improves speed and reduces stress.
Suggested Tool: Asana
Asana offers clean Kanban boards, automation, workload views, and timeline options that help teams maintain a steady flow and spot delays early.
5. Lean Methodology in Project Management
Lean focuses on efficiency, waste reduction, and continuous improvement, originally inspired by the Toyota Production System. It is ideal for organizations that want to improve productivity and create a culture of ongoing improvement.
- Adoption: Used by over 50,000 organizations globally, including manufacturing, startups, and operations teams.
- Active Users: Thousands of project managers and team leads in enterprise-level projects rely on Lean principles daily.
- User Ratings: ★4.4 average for productivity improvement and efficiency.
- Pros: Optimizes workflow, reduces costs, promotes continuous improvement, and boosts team productivity.
- Cons: Initial implementation can be resource-intensive; requires stable processes to avoid disruptions.
Lean emphasizes streamlining processes and delivering maximum value to the customer, making it ideal for organizations aiming to cut costs while improving quality.
When to Use Lean:
- You want to optimize workflow and reduce unnecessary effort.
- Continuous improvement and cost reduction are key goals.
Limitations:
- Requires stable processes and inventory to avoid disruptions.
- It can be resource-intensive to implement initially.
Pro Tip: Review your workflow weekly. Removing even one unnecessary step can significantly speed up delivery.
Suggested Tool: Monday.com
Monday.com supports Lean principles through automation, customized workflows, dashboards, and simplified planning tools that help eliminate repetitive and manual work.
6. PRINCE2
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a stage-based, process-driven methodology for large, complex projects. It emphasizes clear roles, accountability, and risk management, making it ideal for government, corporate, and compliance-focused projects. Each stage has defined deliverables and approval points to ensure consistent progress.
- Adoption: Used by over 150,000 organizations globally, including government projects.
- Active Users: Thousands of project managers in enterprise-level projects.
- User Ratings: ★4.2 average for control and accountability.
- Pros: Strong governance, clear roles, stage-based progress.
- Cons: Heavy on documentation; less flexible.
PRINCE2 is a structured, process-heavy methodology in project management for large or complex projects, focusing on risk management, governance, and staged delivery.
When to Use PRINCE2:
- Managing large or complex projects that require structured governance.
- Projects where accountability and clear role definition are essential.
- Projects requiring compliance with regulatory or corporate standards.
Limitations:
- It can be heavy on documentation and bureaucracy.
- Less flexible for projects that require frequent changes.
Pro Tip: Assign clear roles and responsibilities from the start to ensure every stage is tracked and approved properly.
Suggested Tool: Wrike
Wrike offers built-in approval systems, document management, milestones, dependencies, and detailed reporting, perfect for PRINCE2’s structured approach.
7. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a methodology in project management focused on process improvement, defect reduction, and quality control. It uses the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to analyze processes, eliminate inefficiencies, and deliver measurable improvements. Six Sigma is widely applied in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and operations, where precision and data-driven decision-making are critical.
- Adoption: Over 50% of Fortune 500 manufacturing companies use Six Sigma.
- Active Users: Green Belts, Black Belts, and project teams in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
- User Ratings: ★4.3 average for process optimization and quality control.
- Pros: Data-backed decisions, high-quality outcomes, and reduced errors.
- Cons: Requires statistical expertise and trained personnel.
Six Sigma is data-driven, focusing on quality improvement and defect reduction using the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control).
When to Use Six Sigma:
- Projects requiring high precision and minimal defects.
- Teams need measurable process improvement and optimization.
- Operations where data-driven decisions are critical for quality.
Limitations:
- Requires trained personnel (Green Belts, Black Belts).
- Implementation can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
Pro Tip: Track key metrics at every stage; small data shifts often reveal the biggest process improvements.
Suggested Tool: Minitab
Minitab provides statistical analysis, charts, process control tools, and performance metrics, making it essential for data-driven Six Sigma projects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Methodology for Better Results
Selecting the right methodology in project management can shape how smoothly your project runs and how confidently your team works. Each method, Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Lean, PRINCE2, and Six Sigma, brings its own strengths, structure, and way of solving problems. The goal is not to use the trendiest method. The goal is to choose the one that fits your project’s size, speed, clarity, and complexity.
Think of your methodology as the foundation of your entire project. When it matches your goals, planning becomes easier, communication improves, and risks are reduced. Pairing the right method with the right tool makes everything even more effective. It turns ideas into clear plans, keeps tasks visible, and helps your team stay aligned from start to finish.
In the end, the best choice is the one that supports your workflow, respects your timeline, and helps your team deliver consistent results, no matter how simple or complex the project may be.
FAQs
A project management methodology is a structured approach used to plan, execute, and complete projects efficiently. It provides clear processes, roles, and guidelines that help teams stay organized and focused.
Using a defined methodology in project management helps teams reduce confusion, manage risks, and maintain consistency across tasks. It ensures that everyone follows the same framework, improving efficiency and accountability.
Teams should consider project size, complexity, timelines, and stakeholder expectations. Selecting the right approach early helps align workflows with goals and reduces delays or rework later.
Yes, many organizations adopt hybrid approaches by combining elements from different frameworks. This allows flexibility while still maintaining structure where needed.
Modern tools are designed to support various frameworks, including Agile, Waterfall, and Lean. Using the right methodology in project management alongside suitable software improves visibility, collaboration, and overall execution.